If you’ve ever forgotten about a stash only to find it and smoke it several months or a year later, you might have experienced the powerful sedative effects of cannabinol.
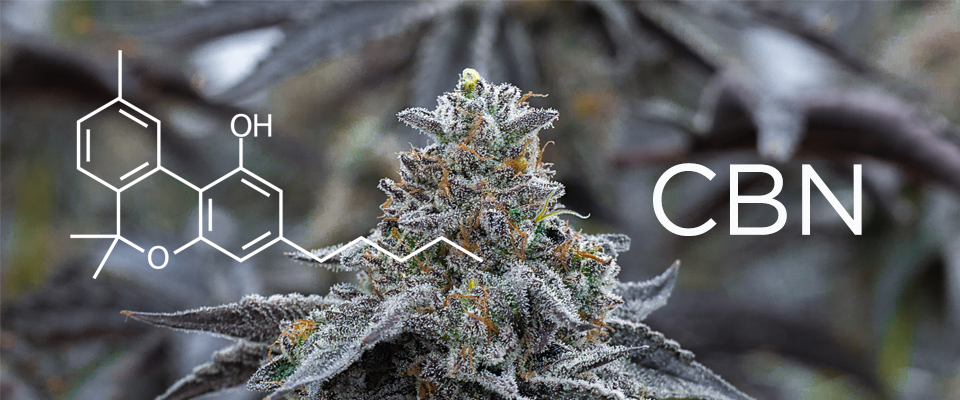
What Is Cannabinol (CBN)?
Just like THC and CBD, cannabinol is another one of the more than 144 cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. But while most cannabinoids start out as Cannabigerolic Acid or CBGA, cannabinol is derived from THCA. Cannabinol is only mildly psychoactive, but it has been shown to offer an array of medical benefits that scientists are only just now beginning to explore.
How is CBN formed? To put it simply, it starts out as THCA. When Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid or THCA oxidizes and begins to break down, it loses some of its molecular bonds and is converted into cannabinol. You probably know that THCA is the precursor to THC, the primary psychoactive ingredient in cannabis. But did you know that as it naturally degrades over time it loses some of its psychoactive properties and converts to CBNA (cannabinolic acid)? Once CBNA is decarboxylated (i.e. burned or heated), it will convert to CBN or cannabinol.
Cannabinol has been called the sleep cannabinoid, and while it does have significant sedative properties, making it a very good treatment for insomnia and inflammation, CBN has been shown to work as an anticonvulsant and to boost immune function. It has also been shown to get you more intoxicated when combined with THC. In a study conducted in 1975, volunteers reported that CBN on its own had barely noticeable effects, when combined with delta-9 THC, it gave users more of a “drugged, drunk, dizzy, and drowsy” effect than just delta-9 THC alone. This is a prime example of what many people refer to as the “entourage effect”, the phenomenon of cannabinoids working more effectively when they are combined with each other.
In the U.S., the prevailing trend has been to dry cannabis as quickly as possible to get it to market. Most U.S. consumers want bright green, dense buds with strong odors and high concentrations of THC. In Amsterdam, it is more common to find the cannabis that has been “cured” for 60 to 90 days after harvesting. This results in drier buds that have a brown or darker green appearance. It also results in higher concentrations of CBN and is potentially more intoxicating.
All of this means that depending on the desired effects if stored properly, cannabis can actually become MORE effective for certain ailments if stored for significant periods of time. In the future, as we learn more about the benefits of CBN and other chemical changes that cannabis undergoes as time passes, it might become popular for moderately “aged” cannabis to be sold in the same way that aged wine or whiskey is sold.
Currently, CBN is more difficult to find in commercial products when compared to other more popular cannabinoids, but we expect this to change as time passes and more consumers begin to seek out non-psychoactive extracts to treat insomnia and pain.